

Embryonic stem cells are present within the embryo, which divides and differentiates into germ layers as they become specialized.These do not, however, contribute to the extraembryonic cells like the placenta. These cells are pluripotent, meaning they can develop and differentiate into various cell types (approx 250 types) during their proliferation.The blastocyst stage in embryonic development is reached within 4-5 days after fertilization, and the number of cells at that point is about 50-150.Embryonic stem cells are a group of cells that are present in the inner cell mass of the embryo at a very early stage of development, called a blastocyst.Kohn by TED-Ed.ĭepending on the source of the stem cells or where they are present, stem cells are divided into various types 1. A major challenge in cell culture is the control and the maintenance of well-defined cell culture conditions, especially the pH and oxygen pressure.During culture, cells are usually passaged under a laminar flow hood and maintained in incubators which are under atmospheric partial oxygen pressure.Different media and conditions are to be employed, considering the purpose of the culture where some cultures might be done to keep the cells in their stem-state while others might want the cells to be differentiated.The culture of stem cells might be different from that of other cells as some stem cells require non-standard cell culture reagents, such as feeder cell layers, conditioned media, or growth matrices.The process of stem cell culture should be refined throughout the process as stem cells always balance between self-renewal and differentiation.Similarly, cell culture parameters need to be refined according to the ultimate purpose of the stem cell culture.cell culture requirements for embryonic stem cells (ES) or different kinds of adult stem cells may not be the same.

Stem cell culture conditions must be refined according to the stem cell type, e.g.Because of this reason, embryonic stem cells are mostly cultured to obtain more embryonic stem cells.

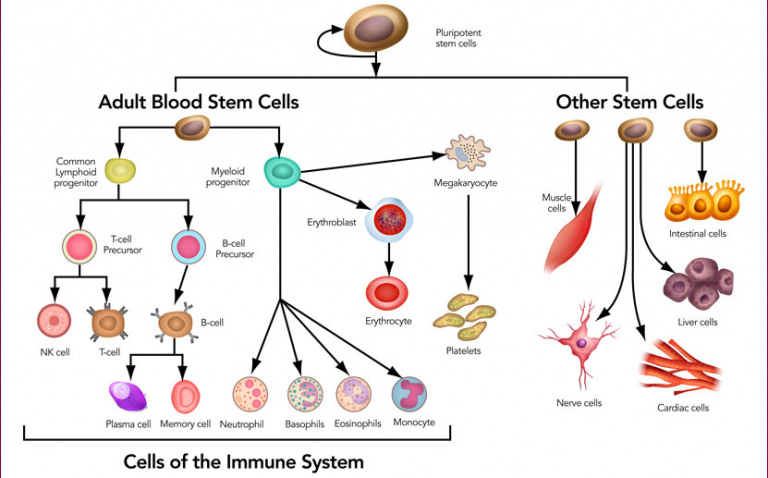
Stem cells have been of great interest as a therapeutic method for various diseases and conditions.These cells provide a continuous supply of new cells that make up the tissues and organs of animals and plants.These cells are the earliest cells of the cell lineage in all tissues and are found in both embryonic and adult organisms.Stem cells are essential cells that replace damaged cells or cells lost due to diseases.Stem cells are unique cells present in the body that have the potential to differentiate into various cell types or divide indefinitely to produce other stem cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
